Ergonomics
What Is Ergonomics
* Ergonomics is the science of fitting the job to the worker. When there is a mismatch between the physical requirements of the job and the physical capacity of the worker, work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs) can result.
Unsafe Situations
Repetitive tasks
Improper posture
Improper lifting
Poor tool design
Poor lighting and glare
Noise
Temperature extremes.
Improper posture
Improper lifting
Poor tool design
Poor lighting and glare
Noise
Temperature extremes.
Twelve Principles Of Ergonomics
1- Keep everything in easy reach
2- Work at proper heights
3- Reduce excessive force
4- Work in good postures
5- Reduce excessive repetition
6- Minimize fatigue
2- Work at proper heights
3- Reduce excessive force
4- Work in good postures
5- Reduce excessive repetition
6- Minimize fatigue
Continued
7- Minimize direct pressure
8- Provide adjustability and change posture
9- Provide clearance and access
10- Maintain a comfortable environment
11- Enhance clarity and understanding
12- Improve work organization
8- Provide adjustability and change posture
9- Provide clearance and access
10- Maintain a comfortable environment
11- Enhance clarity and understanding
12- Improve work organization
1- Keep Everything in Easy Reach
Keep products, parts, and tools that are frequently needed within easy reach.
Long reaches often cause you to twist, bend, and strain which in turn makes work more difficult.
Long reaches often cause you to twist, bend, and strain which in turn makes work more difficult.
Easy Reach
Work At Proper Heights
A common workplace problem is a mismatch in heights between employees and the work that they are doing.
This leads to a poor postures and unnecessary work.
This leads to a poor postures and unnecessary work.
Proper Heights
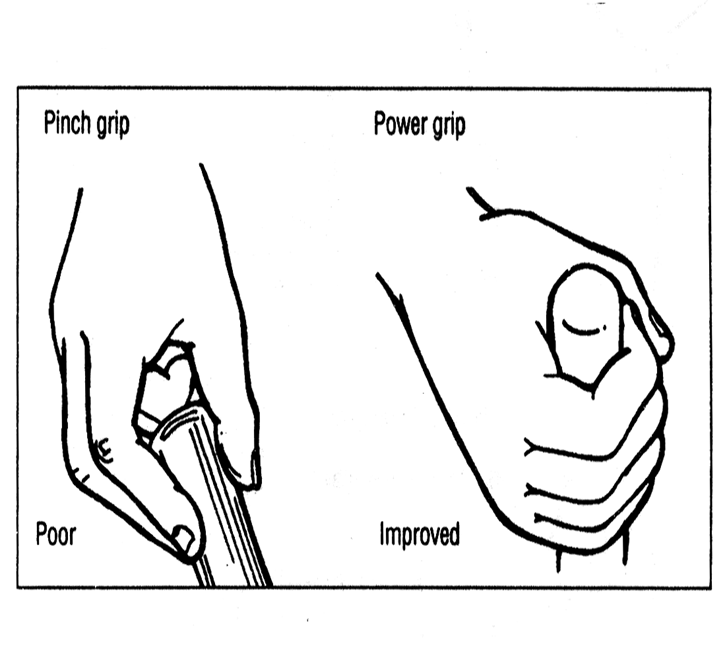
3- Reduce Excessive Forces
Excessive forces load the muscles, creating a potential for fatigue and injury.
Power grips are less stressful than pinch grip.
Use tool grips that are neither too wide nor too small.
Power grips are less stressful than pinch grip.
Use tool grips that are neither too wide nor too small.
Reduce Excessive Forces
Reduce Excessive Forces
4- Work In Good Posture
Use tools, equipment, and workstation layouts that allow you to work in the best possible posture.
Good posture reduces the stress on your body and makes it easier for doing the job.
Good posture reduces the stress on your body and makes it easier for doing the job.
Work In Good Posture
5- Reduce Excessive Repetition
Minimizing the number of motions required to do a task reduce the wear and tear on your body.
Allow machines to do repetition for you.
Allow machines to do repetition for you.
Reduce Excessive Repetition
6- Minimize Fatigue
Overloading your physical and mental capabilities can contribute to injuries, accidents, poor quality
Good design of your jobs can help prevent undesirable fatigue.
Good design of your jobs can help prevent undesirable fatigue.
7- Minimize Direct Pressure
Direct pressure is uncomfortable.
It can inhibit nerve function and blood flow.
It commonly affects :
Palm of the hands
Forearms
Thighs
It can inhibit nerve function and blood flow.
It commonly affects :
Palm of the hands
Forearms
Thighs
Minimize Direct Pressure
8- Provide Adjustability and Change of Posture
Adjustability makes it easier to customize your workstation to fit your needs.
Maintain better heights and reaches and to avoid pressure points and awkward postures.
Maintain better heights and reaches and to avoid pressure points and awkward postures.
Continued
9- Provide Clearance and Access
It is important that you have both adequate workspace and easy access to everything you need.
Clearance is needed for your: Head, Arms, Feet, Knees, Torso.
Clearance is needed for your: Head, Arms, Feet, Knees, Torso.
Clearance and Access
10- Maintain a Comfortable Environment
Seek to create surrounding conditions that enhance your ability to get the job done.
Appropriate Lighting
Avoid Temperature Extremes
Isolate Vibration
Appropriate Lighting
Avoid Temperature Extremes
Isolate Vibration
Comfortable Environment
11- Enhance Clarity and Understanding
Mistakes and errors may result from poor design of the displays and controls you use.
The configuration and layout of these displays and controls can enhance or hinder your performance.
The configuration and layout of these displays and controls can enhance or hinder your performance.
12- Improve Work Organization
Improvements can be made in the system which your work is organized.
Plan, Be involved, Communicate, Enlarge jobs, Be part of the team, Be considerate.
Plan, Be involved, Communicate, Enlarge jobs, Be part of the team, Be considerate.
Cumulative Trauma
One of the important goals of ergonomics is to prevent a type of disorder called “cumulative Trauma”
Wear and tear on the tissue surrounding your joints.
Wear and tear on the tissue surrounding your joints.
Symptoms of CTD
Limited range of motion
Stillness in joints
Numbness or tingling sensations
Popping and cracking in the joints
Redness, swelling, and local skin warmth
Weakness and clumsiness
“Burning” sensations
Stillness in joints
Numbness or tingling sensations
Popping and cracking in the joints
Redness, swelling, and local skin warmth
Weakness and clumsiness
“Burning” sensations
Risk Factors
Repetition
Force
Awkward Postures
Direct Pressure
Vibration
Temperature Extremes
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Force
Awkward Postures
Direct Pressure
Vibration
Temperature Extremes
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Good Posture
Work Station
Erg
Seated – Work Range












































No comments:
Post a Comment